[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Recently, the research team of Tang Jie, the State Key Laboratory of Transient Optics and Photonics Technology at Xi'an Opto-Mechanical Research Institute, made breakthrough research progress in the research and development of low temperature plasma devices. large-scale uniform laminar plasma jet array enhanced by V–I characteristic modulation in a non-self-sustained atmospheric discharge â€was published online in the international comprehensive academic journal Advanced Science“ Advanced Science â€(IF: 15.8 @ 2018, SCI a district). This research achievement is the first time that our institute has published a high-level research paper with an impact factor greater than 15 in the first unit, marking an important breakthrough in the field of frontier basic science research and accelerating the pace of application in our plasma field.
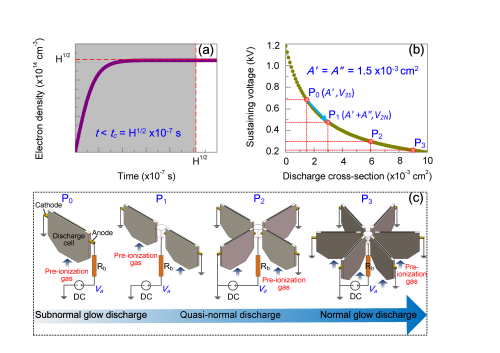
Low temperature plasma has important application value in the fields of biomedicine, material preparation, thin film deposition, and nanoparticle manufacturing. In recent decades, in terms of low-temperature plasma technology, in order to improve the efficiency of the plasma jet, people have been committed to the research and development of a large area uniformly dispersed plasma jet. Plasma arrays are a common method, such as one-dimensional linear comb-shaped plasma jet arrays, two-dimensional honeycomb plasma jet arrays, and two-dimensional square lattice plasma jets. In most cases, these array discharge cells use a dielectric barrier discharge (DBD) structure, and the resulting cross-sectional size of the plasma jet is limited to the order of square millimeters. Because the electrodes and the dielectric barrier are provided between the discharge cells, the spacing between the jets can reach several millimeters or even tens of millimeters. This structural feature greatly reduces the uniformity of the plasma jet, which easily leads to uneven or incomplete surface treatment of the sample, resulting in missed work errors, thereby reducing the working efficiency and quality of the plasma jet. In addition, using inexpensive argon as a working gas, in a structure similar to a DBD discharge, it is extremely easy to form filaments, hindering the formation of a uniformly dispersed plasma. In order to obtain a stable and dispersed plasma, the above-mentioned array device often uses expensive helium as a working gas, which increases the operating cost to a large extent. Using argon as a working gas and using DC glow discharge to obtain a diffused plasma is an effective method. However, DC glow discharge will generate a large amount of Joule heat in the current-limiting resistor and the discharge space, causing a large loss of energy and reducing the efficiency of energy use. Therefore, the research and development of low-cost, low-power, large-area, uniformly-diffused plasma jets has always been a very challenging problem that is still pending in front of people.
In response to the above-mentioned scientific and technical issues, researcher Tang Jie's research group proposed a theory and method of volt-ampere-modulated enhanced gas discharge. Based on this theory or method, the traditional plasma jet has a small volume size, poor uniformity, and low work efficiency. Due to its limitations, a low-temperature plasma jet array with an atmospheric atmospheric pressure dielectric barrier discharge enhanced DC alternating electrode was designed and developed. In this work, for the first time, the volt-ampere characteristics of a DC glow discharge was used to enhance the volume, chemical activity, and working efficiency of the plasma jet. The key points are:
1) According to the modulation theory of voltammetric characteristics, under non-self-sustained discharge conditions, a parallel method is used to increase the discharge cross-sectional area and reduce the sustaining voltage, and successfully achieve the transition from sub-glow to glow discharge mode to achieve the purpose of enhanced discharge;
2) Use cylindrical arc electrodes to optimize the electric field distribution, reduce the electric field difference between units, and achieve continuous and stable discharge of the plasma jet array;
3) The discharge circuit adopts a parallel nesting design method and a strategy of alternately arranging positive and negative electrodes in space to enhance the uniformity of the plasma.
Based on the above-mentioned key technologies, the bottleneck problem of simultaneously obtaining low cost, low power consumption, large area, and uniformly dispersed plasma jet in DC glow discharge is solved. The results show that the width of the plasma jet is increased from the original 15 mm to 90 mm, and the uniformity of the plasma jet is increased from the conventional level of 30% to 97%. Through the voltammetry modulation method, the discharge power is reduced to the original In 65% of cases, the plasma jet length increased by almost 4 times. The research results will play an important role in promoting the application of low-temperature plasma technology.

This work has received strong support from the National Natural Science Foundation of China, Young Scholars of the Western Academy of Sciences (A), and the Open Fund of the Key Laboratory of Spectrum Imaging Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences.
Workpiece Probe,Tool Setting Instrument,Tool Setter,Renishaw Workpiece Probe
Dongguan Liyang Intelligent Technology Co., Ltd , https://www.leyocncmachine.com