- Model NO.: EPH-JII
- Head Style: Round
- Application: Machinery
- Wheel Hub Bolt/U Bolt/C-Bolt/Wheel Nut/Lock Bolt: Wheel Hub Bolt, U Bolt, C-Bolt, Wheel Nut, Lock Bolt
- Transport Package: Carton
- Origin: Qingdao
- Material: Metal
- Standard: DIN, JIS
- Over 15 Years of Experience in Machining Products: ISO9001:2000
- Trademark: EPH
- Specification: OEM/ODM
- HS Code: 8708508600
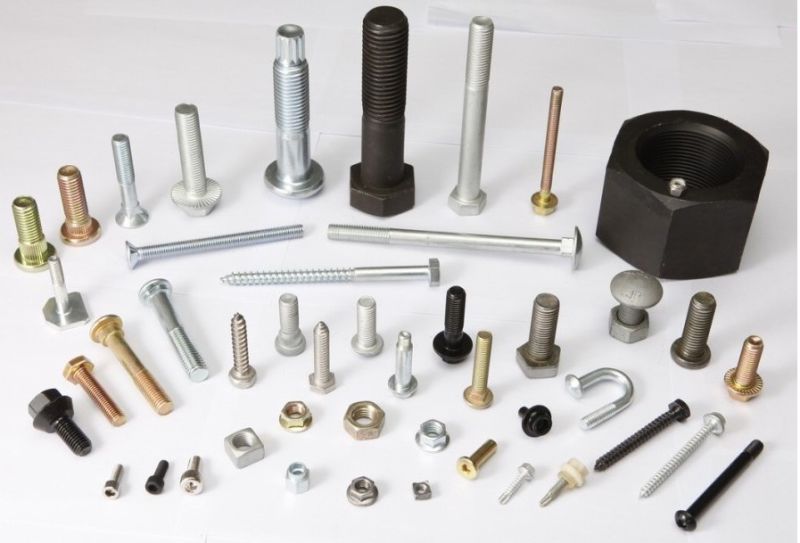

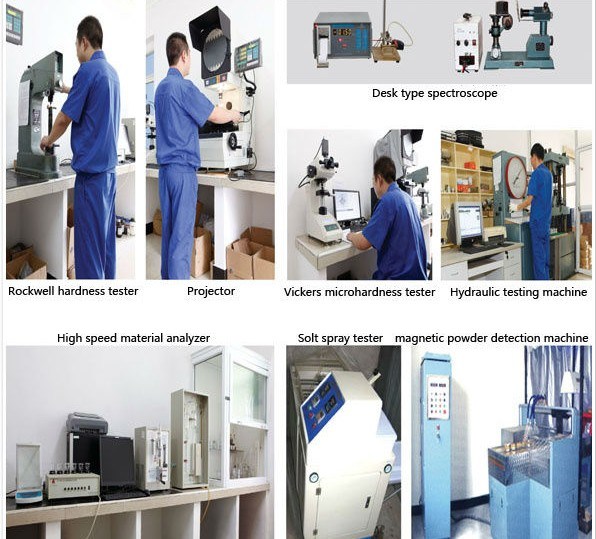

Specifications
| Main Products | Hex Head Bolt | DIN931, DIN933, DIN960, DIN961, ISO4014, ISO4017 | ||
| Heavy Hex Bolt | DIN6914, DIN7990, ASTM A325, ASTM A490 | |||
| Hex Nut | DIN934, DIN6915, ASTM A194 2H, ASTM A563 | |||
| Washer | DIN125, DIN127, DIN6916, ASTM F436 | |||
| Stud Bolt | DIN975, ASTM A193 B7 | |||
| Standard | DIN, ISO, ANSI, ASME, BS, AS, JIS, and Non-Standard | |||
| Application | Building, Instruments, Automobiles, Furniture, etc. | |||
| Grade & Material | Grade 4.8 | Q235 | ||
| Grade 5.8 | 35K (No Heat Treatment) | |||
| Grade 8.8 | D ≤ M20 | 35K | ||
| M22 ≤ D ≤ M24 | 45# | |||
| D ≥ M27 | 40Cr | |||
| Grade 10.9 | D ≤ M24 | 40Cr | ||
| D ≥ M27 | 35CoMoA | |||
| Grade 12.9 | D ≤ M24 | 35CoMoA | ||
| D ≥ M27 | 42CoMoA | |||
| Diameter | M4 - M100mm or 1/4" - 1-1/2" | |||
| Length | 20 - 1000mm or 3/4" - 12" | |||
| Production Process | Cold Heading | Cold heading → Heat treatment → Surface treatment | ||
| Hot Forging | Cutting → Chamfering (tail) → Hot forging → Chamfering (head) → Polishing → Backspin → Threading rolling → Heat treatment → Surface treatment | |||
| Finish | Plain, Black Oxidized, Zinc Plated (White, Yellow, Blue, Colorful), Hot Dip Galvanized, Dacromet, Chrome | |||
| Packing | 25kg per carton, 36 cartons per pallet, or as per your request | |||
| Supply Ability | 800 tons per month | |||
| Minimum Order | 500kgs per specification | |||
| Delivery | 15 - 45 days | |||
| Certification | ISO9001-2008 and Ningbo Product Quality Inspection | |||
| Our Motto | High Quality, Competitive Price, Timely Delivery, Customer First | |||
Curing agents, also known as hardeners, are essential components of many polymer systems, including Epoxy Resins. Curing agents react with the epoxy resin to form a three-dimensional crosslinked network, resulting in a cured polymer with improved mechanical properties, chemical resistance, and thermal stability.
There are several types of curing agents, each with its own unique properties and applications. The most common type is amine-based curing agents, which react with the epoxy functional group to form a secondary amine and an alcohol. This reaction is exothermic and can be accelerated by heat, making it ideal for high-temperature applications.
Another type of curing agent is anhydride-based, which react with the epoxy group to form a cyclic acid anhydride and a hydroxyl group. These curing agents are typically used in applications where water resistance is critical, such as marine coatings and adhesives.
Other types of curing agents include phenolic, acid, and catalytic curing agents. Phenolic curing agents are used in high-temperature applications, while acid curing agents are used in low-temperature applications. Catalytic curing agents are used to accelerate the curing process and are typically used in combination with other curing agents.
The choice of curing agent depends on the specific application requirements, such as cure time, cure temperature, and final properties of the cured polymer. It is important to choose the correct curing agent to ensure that the final product meets the desired specifications.
In summary, curing agents are essential components of many polymer systems, including epoxy resins, and play a critical role in improving the mechanical, chemical, and thermal properties of the cured polymer. The choice of curing agent depends on the specific application requirements and must be carefully considered to ensure the final product meets the desired specifications.
Curing Agent,Epoxy Curing Agent,Curing Agent Coating,Polyether Amines
Shanghai Shengduan Trading Co., Ltd. , https://www.shsdchem.com