[ Instrument Network Instrument R & D ] Organic-inorganic hybrid perovskite has attracted the attention of researchers all over the world for its excellent optoelectronic properties. The solar cell prepared as an active layer has a photoelectric conversion efficiency of more than 25%, which is close to the highest value of a single crystal silicon cell. However, perovskite thin films prepared by the low-temperature solution method are usually polycrystalline.
Perovskite refers to a class of ceramic oxides with a molecular formula of ABO3; such oxides were first discovered as calcium titanate (CaTiO3) compounds found in perovskite ore, hence their names. Because these compounds have many characteristics in structure and are widely used and studied in condensed matter physics, physicists and chemists often refer to them by the ratio (1: 1: 3) of each compound in their molecular formulas. Name "113 Structure". Cube-shaped. Cube crystals often have parallel fringe stripes, which are the result of clustered twins when the high-temperature variant is transformed into a low-temperature variant.
Polycrystalline thin films, which are prone to defects on their surfaces and grain boundaries, will trap photo-generated charges and cause additional non-radiative recombination energy loss, limiting the open circuit voltage and overall performance of the device. Passivation is an effective method to reduce defects and inhibit non-radiative recombination. Lewis base, PbI2, PMMA polymer materials, etc. have been successfully applied to passivate the defects of perovskite. Organic amine salts such as phenethylamine iodide (PEAI) have also been successfully used to passivate the perovskite surface and increase the open circuit voltage of the device. However, PEAI-treated perovskites are sensitive to temperature. At high temperatures, PEAI itself will react to form two-dimensional perovskites, which affects the stability of the device. In addition, the passivation mechanism of ammonium salts needs more research.
Passivation refers to the process in which a metal is oxidized by a strong oxidant or electrochemical method to make the surface inactive, that is, a passive state. It is a method to convert the metal surface to a state that is not easily oxidized, and to delay the corrosion rate of the metal. In addition, an active metal or alloy, in which the chemical activity is greatly reduced and becomes a noble metal state, is also called passivation.
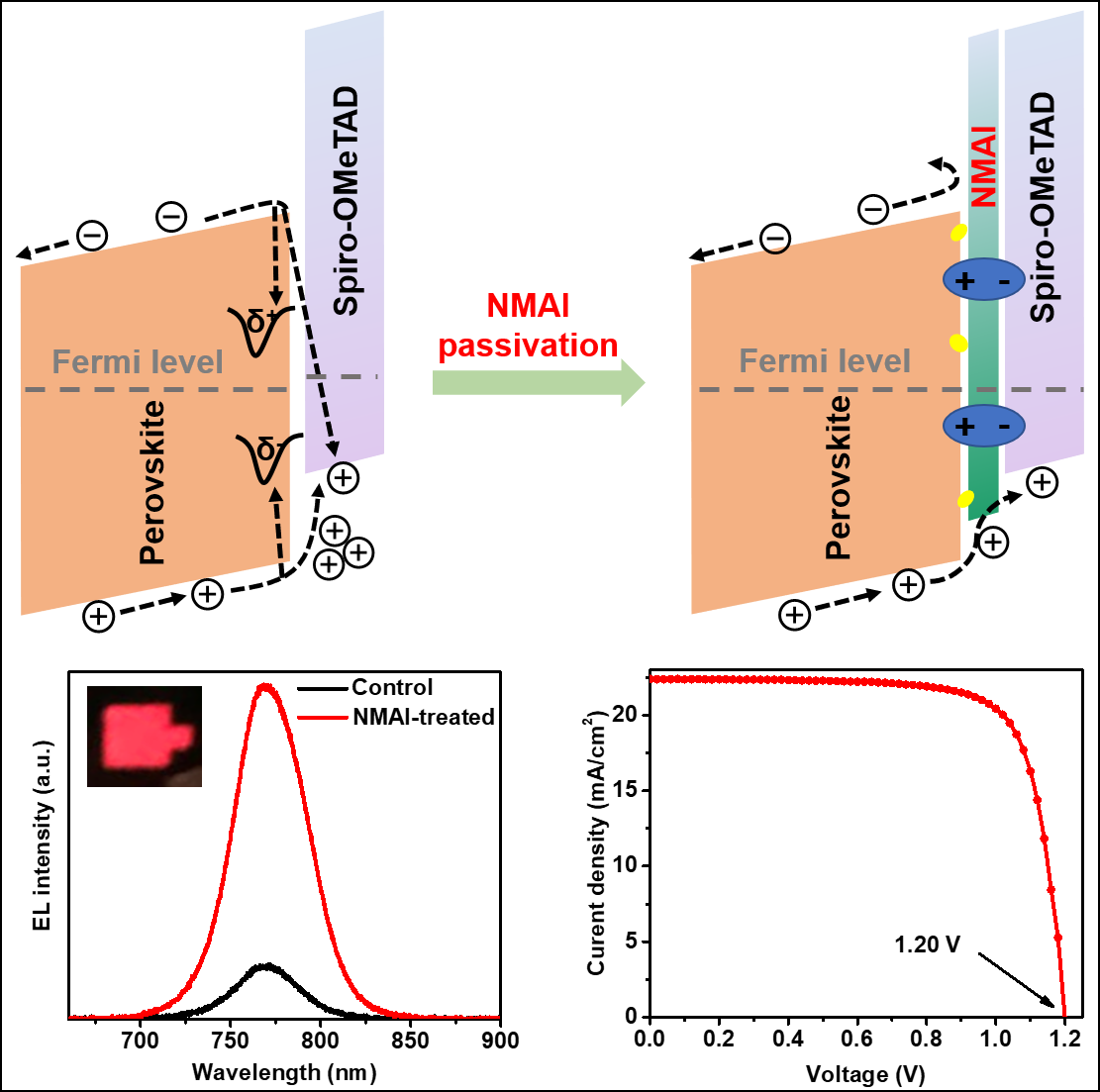
Gao Peng's group at the Key Laboratory of Functional Nanostructure Design and Assembly of the Fujian Institute of Research on the Structure of Matter of the Chinese Academy of Sciences uses a large volume of 1-naphthylmethylamine iodide (NMAI) to passivate the perovskite surface interface. Like PEAI, NMAI is mixed with PbI2 in a strong polar dimethylformamide (DMF) solution and spin-coated in one step to form 2D perovskites, and has been successfully applied to prepare efficient 2D / 3D perovskite LEDs. Device. However, NMAI showed different properties from PEAI when post-processing 3D perovskite films in weakly polar isopropyl alcohol (IPA) solution. XRD tests show that even at high temperatures up to 100 ° C, most of the ammonium salts on the surface of the treated 3D perovskite film did not participate in the ion exchange reaction, and only a very small amount of 2D perovskite was formed.
Therefore, in a complete battery device, the NMAI layer between the perovskite and the hole transport layer plays the following synergistic passivation effects: First, the zwitterionic nature of NMAI itself can passivate the surface ions Defects; Secondly, NMAI interacts with the surface of the perovskite to form an interface dipole, which induces bending of the vacuum energy level, thereby improving the band matching of the interface. Finally, the insulating NMAI can act as an electronic barrier. The multiple passivation effect of the NMAI layer makes the prepared perovskite battery device exhibit higher electroluminescence efficiency, which strongly shows that the non-radiative recombination at the interface between the perovskite and the hole transport layer is greatly reduced. Under a standard sunlight, the open-circuit voltage of the device can reach a maximum of 1.20 V, and the photoelectric conversion efficiency can exceed 21%.
Photoelectric conversion is the process of directly converting solar radiant energy into electrical energy through the photovoltaic effect. The principle of this process is that photons transfer energy to electrons and cause them to move to form an electric current. There are two ways to solve this process. The most common one is to use a solid device with silicon as the main material, and the other is to use photo-sensitive dye molecules to capture the energy of photons. Dye molecules absorb photon energy and separate negatively charged electrons from positively charged holes in the semiconductor.
This work provides new ideas and understanding for the passivation of ammonium salts, and provides guidance for the further improvement of the efficiency of perovskite solar cells.
Source: Fujian Institute of Material Structure, Encyclopedia
Kymco Motorcycle
Kymco Motorcycle,KYMCO Engine Spare Parts,KYMCO Complete Engine Parts,KYMCO Body Kit
SONORA MOTOR COMPANY , https://www.sonoramotor.com