Last updated on March 31, 2023
Figuring out exactly how long it takes to charge an electric vehicle can be a bit tricky, as it depends on several factors. To provide a rough estimate, here's a breakdown of typical charging times:
How Long Does It Take to Charge an Electric Car?
- Using a fast charging station (level 3 charging): On average, it takes between 17 and 52 minutes to charge a medium-sized EV.
- Using a home charging station (level 2 charging): The average time to charge a medium-sized EV ranges from 1 hour and 45 minutes to 6 hours.
- Charging your car without a charging station (level 1): Using a regular outlet at home takes approximately 19 hours to fully charge a medium-sized EV.
*Approximate time to charge the battery from 20% to 80% state of charge (SoC). For illustrative purposes only: Does not reflect exact charging times, some vehicles will not be able to handle certain power inputs, and/or do not support fast charging.
Electric Cars: A New Experience for Many
With electric mobility gaining traction, the global EV market is expected to reach a value of $190 billion by 2030. However, for many, electric vehicles remain a relatively new concept, filled with uncertainties. Price and range are often top concerns, but one of the biggest questions revolves around charging times. Research conducted with Ipsos shows that 30% of potential EV buyers are worried about the time required to charge an electric car. We aim to address these concerns by providing a clear overview of typical charging durations.
Charging Times for Electric Vehicles
|
EV Charging Level |
Power Output Charging Session |
Small EV |
Medium EV |
Large EV |
|
Level 1 |
2.3 kW |
11h36m |
18h50m |
26h05m |
|
Level 2 |
7.4 kW |
3h36m |
5h51m |
8h06m |
|
Level 2 |
11 kW |
2h25m |
3h56m |
5h27m |
|
Level 2 |
22 kW |
1h08m |
1h45m |
2h27m |
|
Level 3 |
50 kW |
32 min |
52 min |
1h12m |
|
Level 3 |
100 kW |
16 min |
26 min |
36 min |
|
Level 3 |
150 kW |
- |
17 min |
24 min |
|
Level 3 |
240 kW |
- |
11 min |
15 min |
|
Level 3 |
300 kW |
- |
8 min |
11 min |
|
Approximate time to charge the battery from 20% to 80% state of charge (SoC). For illustrative purposes only: Does not reflect exact charging times, some vehicles will not be able to handle certain power inputs, and/or do not support fast charging. |
||||
How Long Does It Take to Charge My Electric Car?
If you want to know the charging time estimation for your specific electric car or any model you have in mind, use our free electric car charging specifications tool.
But what influences EV charging times? The answer isn’t as straightforward as you might think. Several factors determine how long it takes to charge an electric car.

Electric Cars vs Gas Cars
If you're reading this article, chances are electric mobility is still new to you. Understanding how the "refueling mindset" of an EV differs from that of a gas-powered vehicle is crucial. Gas vehicle drivers typically fill up their tanks when the fuel gauge approaches empty. For EVs, however, most drivers prefer to top up their batteries whenever they park. This practice, known as opportunistic charging, allows you to make the most of parking time at home, work, or shopping centers to keep your battery topped up. Additionally, it's a battery-health-friendly approach to avoid fully draining your battery before recharging. While charging an EV does take longer than filling a gas tank, in most cases, you won't notice since you'll be busy doing other things.

What Impacts Electric Car Charging Time?
1. Battery Size
Just like the size of a gasoline car’s tank, the size of a vehicle’s battery determines how much energy it can hold. Measured in kilowatt-hours (kWh), the electric equivalent of a liter or a gallon, the larger the battery, the longer it will take to charge. Larger vehicles, such as the Porsche Taycan or Tesla Model S, with battery capacities of 90 kWh and 100 kWh respectively, take longer to charge at the same power output than smaller vehicles. However, once full, these larger batteries allow you to travel farther than those with smaller batteries.
2. State of Charge (Empty vs. Full)
Similar to a fuel gauge in a gas-powered vehicle, the state of charge (SoC) refers to the percentage of energy your EV can use between 'full' and 'empty.' Simply put, it’s the percentage charge your EV battery holds relative to its capacity at a given time. Due to battery chemistry, a battery with a low SoC can accept a much higher power output than one with a high SoC. As illustrated in the graph below, charging slows down as an EV’s battery approaches full capacity. This is why charging an EV from 20% to 80% is much faster than from 80% to 100%.
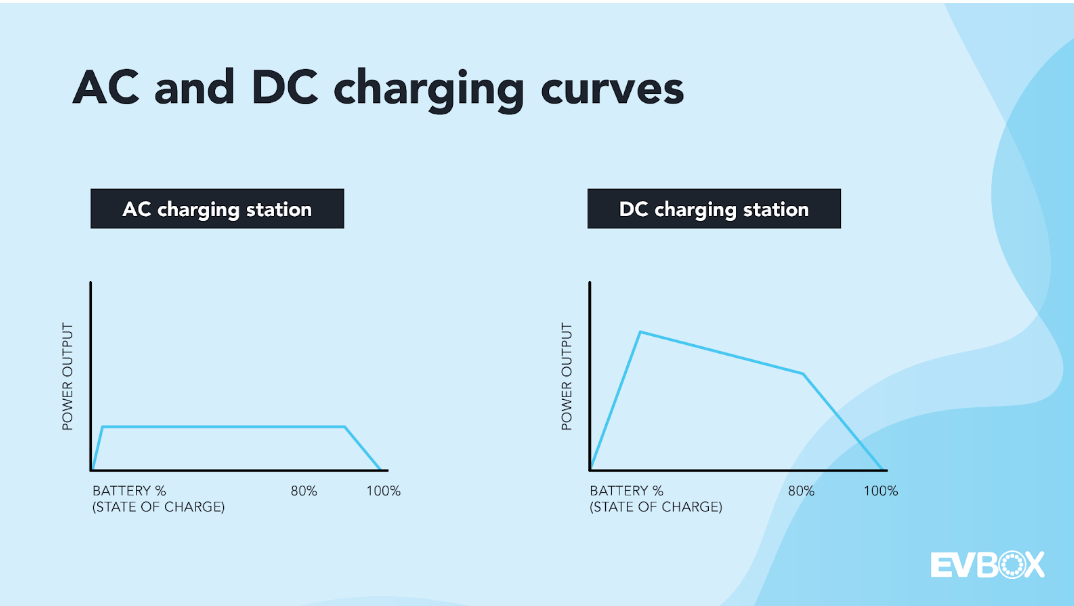 Â
Â
3. Charging Capacity of the Vehicle
While larger batteries can store more power, they don’t always mean faster charging times. Some vehicles can take higher power inputs than others. For instance, the Tesla Model 3 has a fast charging capacity of 250 kW, whereas the smaller Peugeot e-208 only supports 50 kW fast charging—a significant difference in charging times. Therefore:
- Charging a Peugeot e-208 at a 240 kW charging station effectively means it charges at a maximum of 50 kW, as that’s all it can take.
- Charging a Tesla Model 3 at the same 240 kW station means it will charge at a maximum of 240 kW, even though the car can take 250 kW, as that’s the maximum output of the charging station.
As a result, a small battery doesn’t necessarily mean a vehicle will charge faster. Although the Tesla’s battery is larger than the Peugeot’s, it will take less time to charge when using fast charging.
4. Weather Conditions
Environmental conditions, particularly temperature, play a critical role in charging speed. Batteries operate most efficiently between 20–25°C (68–77°F). When temperatures are too low or too high, charging may take slightly longer, especially with fast chargers. This happens because a vehicle’s battery management system (BMS) reduces power to protect the battery from extreme temperatures.
5. Power Output
There are different levels of charging, and generally, the higher the level, the faster it can charge your vehicle. Let’s take a look at each to see how they compare.

Electric Car Charging Times for All EV Charging Levels
Level 1 Charger
What Is a Level 1 EV Charger?
Level 1 charging refers to plugging the cable that came with your EV into a standard household socket.Â
EV Level 1 Charging Time
Charging via a domestic socket is the slowest way to charge an EV. Standard household outlets deliver up to 2.3 kW (10 A). This equates to around 4 to 5 miles of range per hour (6 to 8 kilometers). For example, it would take 24 hours and 30 minutes to fully charge a 50 kW Peugeot e-208 on a Level 1 charger. This method is not only slow but can even be dangerous due to the lack of protection against power overloads. Learn why we don’t recommend this charging method.
Level 2 Charger
What Is a Level 2 EV Charger?
Level 2 charging refers to charging your EV via a dedicated charging station that is specifically wired into your home or building’s power supply. Given their cost and speed, Level 2 chargers are commonly found in residential and commercial locations.

EV Level 2 Charging Time
Depending on the power output and the vehicle type, charging on a Level 2 charging station is roughly 5 to 15 times faster than charging via a regular socket.Â
Level 2 chargers come in a range of charging capacities. Charging for an hour with a 7.4 kW charger delivers about 25 miles (40 kilometers) of range, an 11 kW charger about 37 miles (60 kilometers) of range, and a 22 kW charger around 75 miles (120 kilometers) of range. These calculations are estimates based on the average battery use of 18 kWh per 62 miles (100 kilometers).
To put this into perspective, to fully charge a 50 kW Peugeot e-208 on an 11 kW Level 2 charging station would take only 5 hours and 15 minutes—significantly faster than the Level 1 example above.
Level 3 Charger
What Is a Level 3 EV Charging Station?
Also known as DC fast charging, Level 3 charging uses direct current (DC) to charge a vehicle. In short, Level 3 chargers deliver more power, faster, making them ideal for short-stop locations like gas stations and fleet depots. As it’s available at a much higher voltage, it goes without saying that DC chargers are far more powerful than Level 1 and 2 charging.
EV Level 3 Charging Time
As its name suggests, DC fast charging is the fastest way to power an EV, recharging most vehicles in just minutes instead of hours. Level 3 chargers come in many different shapes, sizes, and charging capacities. That, in combination with the many vehicles and battery types out there, means charging speeds and times can vary greatly.Â
The Future of EV Charging
As EV technology continues to advance, it won’t be long before charging electric cars gets even faster. New battery technology and improved fast charging standards are constantly increasing the speeds at which EVs charge, with EVBox’s new DC charging station that can already deliver up to 400 kW charging, which can add up to 100 km of range in just three minutes.Â

Looking ahead, many scientists and engineers are already working on further speeding up charging times. A team of Harvard researchers recently designed a lithium-ion battery prototype that, under laboratory conditions, can recharge over 50% of its capacity in just three minutes—and do so thousands of times without significantly degrading. This, the researchers say, could pave the way for batteries that can recharge fully even faster.Â
Learn More About EV Charging
While there’s no simple answer to how long it takes to charge an electric car, understanding the various variables such as the car, the battery, the charging station, and weather conditions, we hope this overview gives you a good idea of how long it takes to charge an EV.
If you’re interested in learning more about EV charging, or are considering buying an electric car for the first time, have a look at our comprehensive EV charging guide for an overview of everything you need to know.
Car Wireless Charger-Sienna,Premium Car Wireless Charger,Toyota Fast Wireless Charging,Toyota Car Wireless Charger
Changzhou Saina Automobile Industry Co., Ltd , https://www.jsczsaina.com
