Automated disaster prevention measures are difficult Difficulties in process stability Poor process sheets do not meet environmental requirements Operator requirements (Short-term training) High basic knowledge of oxygen probes, infrared instruments Rings are better or not better Special alloys are difficult to make Easy to invest 篼 High cost of operation The low-high vacuum heat treatment uses vacuum technology to reduce the partial pressure of oxygen in the atmosphere, and it is easier to achieve bright heat treatment than controlled atmosphere heat treatment (the impurity content is one to one thousandth less than the controlled atmosphere. Especially from the material The evolved gas is removed from the furnace in a timely manner to prevent oxidation reaction on the surface of the workpiece. m Vacuum heat treatment does not cause surface decarburization, carburization, oxidation reaction; vacuum heat treatment has degreasing, off the surface rust, so that the surface of the workpiece is treated with a high degree of purification And activation, and easy to achieve controlled heating slowly, and rapid cooling, so vacuum heat treatment deformation is very small. Compared with vacuum carburizing, 10U grain boundary oxides are inevitably avoided even at high levels of controlled atmosphere carburization. The controlled atmosphere needs to strictly manage and control the carbon potential and other chemical quantities, while the vacuum heat treatment only requires the control of physical quantities such as pressure, which is easy to automate and the product quality is stable. Vacuum heat treatment can use nitrogen, argon and other inert gases for cooling, safe, pollution-free, without polluting the environment.
Due to the above characteristics, the vacuum heat treatment has the advantage of more controllable atmosphere heat treatment, and due to the characteristics of good quality, small deformation, energy saving, and safety, the international trend of transfer of controlled atmosphere heat treatment to vacuum heat treatment has recently increased. For many special materials, it is required that the vacuum heat treatment is indispensable for the high temperature treatment (>1000C), low temperature treatment (30075 (TC), active metal (such as Chin), or high active material (Ti, Nb) materials. The best choice.
2 heat treatment of stainless steel, heat-resistant steel 2.1 austenitic non-reinforced stainless steel, heat-resistant steel.
Heat treatment purposes: To obtain high corrosion resistance, high plasticity, and to eliminate cold hardening, plasticity recovery should be carried out (or solid solution) treatment.
Process: 105 (TC11501 water, oil, air cooling (depending on the size of the workpiece, effective size, shape).
Application: 0Crl8Ni9 Rolled piece eliminates vacuum hardening for cold hardening: 104CTC, lfTPa, oil cooling.
Treatment results: Bright surface, plastic recovery, can continue processing.
2.2 Martensite can be strengthened stainless steel, heat-resistant steel lCrl3, 2Crl3, 3Crl3, 4Crl3, 9Crl8 and so on. This type of steel can be subjected to the following different heat treatments according to different uses and technical requirements.
A. In order to obtain high strength, high corrosion resistance (quenching + low temperature tempering) B, to obtain the strength and elasticity of crucible (quenching + medium temperature tempering) C, to obtain good mechanical properties and high corrosion resistance (æ³®(Fire + high temperature tempering) D. To remove machining stress, reduce hardness, improve plasticity and toughness (annealable) E, to improve the organization can be normalizing and high temperature tempering (normalizing + high temperature tempering) F, precipitation hardening Stainless steel can be solid solution and aging treatment for good mechanical properties and corrosion resistance.
25mm, or heat treatment of threaded parts, threaded holes, blind hole parts, etc., is recommended to use a vacuum furnace. Requirements for vacuum furnace: When the pressure in the furnace is 9Pa, the rate of pressure rise should not be greater than 0.35Pa per hour. 2.3 Application 2.3.1 Vacuum aging of precipitation hardening stainless steel 0Crl7Ni4Cu4Nb precipitation hardening stainless steel (PH17-4) has excellent corrosion resistance And mechanical properties. Widely used in aerospace products, such as servo valve housings, action cylinders, etc. Due to the presence of Nb and Cu, the surface is easily oxidized during aging in an air furnace. In order to ensure the smoothness and non-oxidation of the parts, vacuum aging is adopted and good results are obtained. The surface of the parts is kept with the metal luster after cutting. The aging process is: 480 to 5801:, vacuum 2.3.2 high speed, corrosion resistant bearings (9Crl8) In order to obtain corrosion-resistant, wear-resistant, high-precision, small deformation of the bearing parts can be vacuum oil quenching + low temperature tempering m.10101070C oil cooling, 3 heat treatment of high-temperature alloy superalloy according to the different elements, points Ni-based, Fe Base, Co base, according to enhanced features, divided into solid solution strengthening and aging strengthening type. An example is given by taking an Ni-based aging-strengthening alloy as an example.
3.1 Models and components Solid solution cooling Conditioning Cooling Air cooling 3.3 Requirements for vacuum furnaces 3.4 Application: Metal bellows for engine end seals. The material is high-temperature alloy GH169, thickness S =. 2nm. The parts are treated with solution after welding and the first aging strengthening treatment, and then the overload test: pressure 0.2MPa, hold for 5 minutes, the parts can not be deformed and wrinkled. A second intensification treatment was then performed, and compression was repeated 10 times or more and the heating test was performed.
Soil 10X: Insulation 0.5h for air cooling; After secondary hardening, room temperature strength 6226MPa (6b 125kgf/mra2h heated in an ordinary electric furnace and air cooling will inevitably severely oxidize. Therefore, we try the vacuum heat treatment for solution treatment, change the air cooling to the furnace Cooling to room temperature, the process is as follows: 0.5h furnace cooling to room temperature; first aging: 72 (TC, 4h, furnace cooling to room temperature: second aging: 620C, 16h, furnace cooling to room temperature; parts with furnace heating , The degree of vacuum is not lower than 1.33Xl (T3Pa. After the above process, the parts are silver-white, no deformation, the strength and plasticity test after the test have reached the material standard. The process test and repeated compression of the parts, the pressurization test are qualified , In order to achieve the vacuum heat treatment of the superalloy GH169 capsule.
13 乇) These easily oxidized elements in the vacuum quenching furnace oxidize very quickly; the quench oil also causes the parts to have different degrees of coloration, so the GH169 solution in this type of furnace has a poorly colored surface.
4 Heat Treatment of Titanium Alloys 4.1 Composition Grade TC4 Stress Relief Annealing 50065r26h Air Cooling Ordinary Annealing 70080r12h Air Cooled Solid Solution 90000.5lh Air Cooling Aging 500X: 26h Air Cooling 2 Recommended Process Vacuum Degree Pressure Rise Rate Insulation, Before Bakeout 4.3 Equipment Requirements Preventing Oxygen , Nitrogen, Hydrogen Contamination 4.4 Application Ti alloy aging, spherical accumulator made with TC4, behind the wall 3nun, the required failure pressure is not less than 66MPa, because the parts are spherical and porous, if the oxidation, cleaning more difficult. After vacuum heat treatment, not only the surface is very bright, but also the material is purified, and the characteristics of the material are fully utilized. Process is 55 (TC, 4h, vacuum degree is not lower than 1.33Xl2Pa. l (r2Pa, after annealing, the surface is bright, the plasticity is in the ordinary annealing furnace.
Causes of Color Titanium is very reactive and easily colored by oxidation. First of all, the equipment factors are very important. It should be noted that the ultimate vacuum is not more than 8×14Pa, and the pressure rise rate is not more than 5×10lPa/h. After the vacuum oven is fully oven-baked, there is no other pollution source in the furnace. If the effect is still not satisfactory, you can find the following reasons from the following eight reasons: 1 before the cleaning, 2 gloves into the furnace with the workpiece, 3 degrees before the vacuum to increase the temperature as much as possible, 4 working vacuum can not be too high, the element volatile, 5 control heating rate, and vacuum Degree of change, try to match, 6 pay attention to cooling gas composition (Ar, N2), impurity gas and moisture should be minimized, 7 furnace temperature 5 vacuum heat treatment of the elastic alloy can be divided into Fe, Ni, Co, Ti, according to chemical composition. Nb base and so on. An iron-based alloy is used as an example to illustrate that this type of alloy is a dispersion-hardened austenitic alloy. The solidified solution has a very good plasticity in the quenched state. It can be molded into parts, strengthened after aging, and has high mechanical strength. Elastic properties, non-magnetic, corrosion resistance. Operating temperature 31 up to 25 (TC, 32 up to 35 (TC, 353 up to 400C, these are all widely used in precision instrumentation, aerospace, aerospace materials).
5.1 Fe-based high-elastic alloy composition Process thickness (mm) Degree of vacuum for cooling medium Water, oil, gas, oil and water 5.2 Recommended process (1) The amount of solid solution can not be too dense, ensure the uniformity of heating and cooling, vacuum degree 1.33 Example X 3 Many parts in electro-hydraulic servo valves are made of 31, such as feedback levers, spring rods, nozzles, baffles, etc. The dimensional accuracy of these parts is relatively high, and the tolerance is sometimes less than 0.003mm. Some parts have a diameter of only 0.8mra. The blind holes in the holes are many in the following and the shape is complicated. The parts are finished after solid solution quenching of the rough material, because the non-complex sizes are not processed anymore, so the heat treatment cannot be oxidized.
31 contains Ti, A1, after heat treatment is very easy to become dark blue, not meet the technical requirements. After treatment with a vacuum furnace, the bright metallic luster can be maintained, and the vacuum annealing treatment of 6 electrician silicon steels is performed. 6.1 Annealing Purpose The purpose of annealing is to eliminate residual stress and work hardening caused by cold working such as rolling, stamping, shearing, and deburring. Improve the organization of carbon from the grain boundary, such as intragranular, grain coarsening. For cold milk silicon steel sheet, texture recovery and magnetic properties can be improved by annealing and recrystallization. Annealing can also purify the material, reduce harmful impurities in the steel and gases such as carbon, sulfur, oxygen, nitrogen, hydrogen, etc. to further improve the magnetic properties of the material.
Vacuum annealing can improve magnetic performance even more than ordinary annealing. After hydrogen annealing, it is also possible to supplement 750C for 2 hours, 1 (vacuum annealing of T2Pa), and magnetic properties are improved due to the removal of hydrogen infiltrated by hydrogen annealing and further degassing.
Material Grade Heating Method Annealing Temperature X: Holding Time h Cooling Medium Ambient DR225 150t: Released Hydrogen or Vacuum DR1250G 150X; Extruded Hydrogen or Vacuum D Take 240 to DW470 Follow-up 80084026 Furnace Cooling Team or Vacuum DQ120 to DQ183 Follow-up 78084026 Furnace Cold team or vacuum DW500 150V furnace cold decarburization or vacuum DG3 400X: fast cooling, 150r furnace vacuum or high n2DG3 to magnesium oxide core with furnace heating up to 150X: baked. Hydrogen Note: The selection of the layer annealing temperature should pay attention to, inorganic coating does not exceed 850C, hydrogen dew point 3 Application Example 7.3.1 DT4A electrical pure iron AX-type relay with a core, armature, iron (referred to as the three iron ) Manufactured using DT4A, the original use of homemade simple vacuum furnace (5X 103Pa) annealing, low vacuum, heating and cooling speed can not be automatically controlled. The processed products have poor lightness, high coercivity, and poor strength and toughness. It is very difficult to adjust the electrical properties of the relay. Sometimes a light tap on the relay assembly will break some of the “triple ironâ€.
The result of the treatment in a regular vacuum furnace is that the brightness is up to 80%, the grain size is increased from 34 to 23, and there is no mixed crystal phenomenon. The coercive force is reduced from 0.92 Oersted to 0.86 Oersted (69 A). /m) 禚 〠〠ã€, 篼 强度 强度The used process 181 is: 3C/min rose to 70 (TC, 1 technical requirements process a process two processes three remarks He ι 77.472.027. 5r/h down to 880X: keep 2h, 10-3Pa. Process 2: heat up with the furnace to 800X:, 75C/h rose to 1000X: Insulation 3h, 50XVh dropped to 890C Insulation 4h, 5 (TC/h dropped to 50r and moved to cooling chamber 150x: After the furnace is released. Vacuum degree l (TPa- process three: in process two After processing again, 11000, 6h, 50C/h dropped to 5,000 and moved to the cooling room 150X: After the furnace is released, its air space is 10>a. From the above process results, it can be seen that the qualified electric iron products can be processed with the vacuum furnace. Because of the high temperature control accuracy and temperature uniformity of the vacuum furnace, the rise and cool rate can be adjusted, and it can be easily handled at high temperatures (>1C).Of course, vacuum and oxygen combined heat treatment will be better for soft magnetic materials. effect.
8 Vacuum Heat Treatment of Copper and Copper Alloys 8.1 Industrial Pure Copper 1.1 Types and Applications Industrial Pure Copper Category Code Oxygen Smelting Method Remarks Industrial Pure Copper Oxygen-free Copper Vacuum Deoxidized Copper Deoxidation Under Atmospheric Pressure 4k Pure Copper Features and Applications Grades Product Types Characteristics Uses Rods, foils S Conductive, thermal, and irradiative. Good processability. There are hydrogen embrittlement wires, cables, detonators, cauldrons, pipelines, etc. Plates, belts, strips, foils, tubes, rods, and wires are slightly more contaminant. There is hydrogen embrittlement.
General copper, switches, washers, gaskets, rivets, nozzles, tubing, pipes.
Plates, strips, strips, tubes, purlins, strips, tubes have high purity, high electrical conductivity, and high thermal conductivity.
No hydrogen disease. Processing, welding, corrosion resistance and cold resistance are good electrical vacuum devices.
Tube, slat welding, process, cold bending. No hydrogen disease. It is not possible to use t-oxidizing gas in voluntary gas.
Supply pipes, gas supply pipes, condensation, evaporators, heat exchangers, train parts.
The wire rod is hot and has no hydrogen disease.
Electro vacuum devices, anodes in vacuum tubes 8.1.2 Vacuum heat treatment Oxygen-containing copper is used in voluntary gas (fat, CO, CH annealing, the phenomenon of automatic embrittlement and cracking is called "disease." This phenomenon is due to During annealing, hydrogen and other gases enter the interior of the copper and react with the oxygen contained in the copper to form high-pressure water vapor or C2 such as: these gases are insoluble in copper and have no diffusion capacity, causing significant pressure in the copper to crack the copper. In the subsequent pressure processing or service process, the brittleness will not occur instantaneously, and there will be a certain incubation period.Oxygen-free copper and deoxidized copper will be heated in the oxidizing gas and then heated in the reducing gas. Hydrogen is produced, so annealing of industrial pure copper products is best performed in a vacuum furnace.
Industrial pure copper (ie, copper) is usually only subjected to recrystallization annealing in order to eliminate internal stresses and soften or refine the grains. Annealing temperature Annealing temperature and holding time of pure copper Product type Brand No. Annealing temperature re) Holding time (min) Dimensions (mm) Tubes Bars Wires Specular copper tubes are necessary for the production of air conditioners and refrigerators. They must have a regular shape. , smooth surface, precise size, and stable performance. In the past, such copper pipes had to be imported. The copper pipe itself has a small pipe diameter (outer diameter of 1020 mm), a thin pipe wall (0.21.8 nun), and a long pipe body. According to the design requirements, the user uses the pipe at 90180 degrees in the mold under normal temperature conditions. When bending, the outer edge surface of the pipe cannot be cracked, and the inner edge of the pipe is lighter and the better. The deviation of the wall thickness should be less than 20%, and at the same time, it should be ensured that no rupture or leakage occurs under the pressure of 7 MPa.
To meet these requirements, the heat treatment of mirror copper tubes should use vacuum heat treatment.
Annealing process: After the charge is cleaned, the vacuum is pumped into the furnace until the 101Tooi heats up, the T2 copper tube is 340C, the soft copper tube of the refrigerator is 350 400'C, the hard half copper tube of the refrigerator is 3003201, and the soft TUP copper tube 4201 is kept in the furnace after 60 minutes of heat preservation. Cold baked below 80C.
Copper foil heat treatment, processing of copper foil for printed circuit boards is a cold rolled strip with a thickness of 0.02mm, must be annealed and softened, and can not be slightly oxidized, heated to 65 in a vacuum furnace (TC, 10lToor heat for 1 hour, furnace Cold baked below 80C, bright surface, good softening effect.
8.2 Brass 8.2.1 Brass Grades and Applications H96, H90, H80, etc. are low-zinc brass, golden yellow, with sufficient strength, good ductility, deep drawability, and corrosion resistance. Used to make heat exchangers and condensers. H90 is used to make hot-rolled bimetals, strips, and thermocouples. H70 and H68 have similar performances. Panax brass is used to make shells, heat exchangers, pipes and electromechanical components. H68 is widely used to make deep-drawn parts, such as heat exchanger shells, bellows and so on. H62(a+0) is easy to cut and weld with pipes and plates for precision manufacturing. H59 is a high-zinc brass, strength, good thermal deformation, used for hot stamping, bar, profiles used in machinery manufacturing and welding rods.
8.2.2 Vacuum heat treatment Brass plate and wire must be annealed several times in the manufacturing process. Bright annealing is usually used to prevent oxidative discoloration and material loss due to oxidation. In this way, it is also possible to eliminate the pickling process that is carried out due to the removal of scale, and to avoid the environmental pollution caused by pickling.
The easy oxidation of brass is mainly due to the presence of zinc. Copper is easily oxidized at high temperatures, but it is hardly oxidized in CO-Q and H2H20-based atmospheres.
However, zinc not only oxidizes in an oxidizing atmosphere, but also generates oxidation in the above two atmospheres. The reaction is as follows: Due to these reactions, dezincification occurs, thereby destroying the shiny surface of the copper article. Therefore, using a vacuum furnace to treat copper products is expected to achieve a bright surface and excellent performance.
H65C> 4, 45 (TC, 10Pa, 3 hours of heat preservation, furnace cooling to 100T: post-baking. Effect: bright surface, uniform color, uniform hardness of inner and outer rings, wide grain size, brass rework rate Zero Strength: 320375N/mm2.8.3 The semi-finished products such as bronze, beryllium bronze, strip, wire rod, and bar are mostly in soft (quenched) and semi-rigid (work hardening) materials. Cold formed parts of various shapes, direct aging strengthening.
Quenching: Beryllium bronze has a high heat treatment strengthening effect. The purpose of quenching is to solid-solubilize the cerium-rich phase and obtain a supersaturated solid solution with precipitation hardening ability. It is prepared for aging strengthening; it can soften work-hardened materials to withstand further Cold deformation, in addition, quenching can also eliminate casting segregation. Quenching heating temperature 775955C, in order to avoid oxidation of the workpiece surface, should be processed in a vacuum furnace. The shorter the quenching transfer time, the better. Aging: The purpose of aging is precipitation hardening. Low-temperature aging: 315345X:,, time 13 hours; high-temperature aging is 35038 (TC, time 1590 minutes. Beryllium bronze spring sheet (thickness 0.15 ~ 0.25 mm), punch a vacuum tempering (Hv> 320), 8.4 other solid solution And aging-enhanced copper alloys 8.4.1 Name and type A, beryllium bronze, B, silicon bronze, C, aluminum bronze, D, titanium bronze, E, chromium bronze, F, zirconium bronze, G, aluminum white copper.
8.4.2 Solid solution (quenching), aging process name and main components solid solution (quenching), aging process use solution temperature (r) aging temperature (r) voice copper electrical springs, contactors, reeds, clockspring, Diaphragm, compass, bearings, bushings and other elastic, wear-resistant parts.
Aluminium-copper high-speed, strong, abrasive milled pinions, bearings, turbines, nozzles and other military components are resistant to corrosion, temperature and wear parts.
Titanium bronze high-strength, elastic, hard, wear-resistant, corrosion, fatigue, heat and other components.
Chrome has high-strength, heat-resistant, grinding, heat-conducting commutator pieces and locomotive overhead lines.
Zirconium bronze is highly conductive and heat; it has high heat resistance and creep strength, electrode materials, and wires.
When aluminum white copper is used for vacuum heat treatment, such as stubbornness, heat resistance, and erosion springs, industrial pure copper is 10010 MPa, and other copper alloys are 1010 lPa. Solution treatment, due to high temperature, vacuum selection can be lower to prevent volatilization. During aging treatment, due to the low temperature, the degree of vacuum can be reduced to ensure bright color. The tapping temperature is controlled at 8010 (TC or less. When dealing with copper alloys with high Zn content, it is necessary to reversely charge nitrogen or argon to prevent dezincification.
9 Vacuum heat treatment of high-purity aluminum foil Pure aluminum foil is the basic material for manufacturing quality electrolytic capacitors. Annealing is a key process in the production of aluminum foil and directly affects the quality and electrical properties of aluminum foil.
The annealing of high-purity aluminum foils in developed countries is directly carried out by the material factory after being manufactured. Many continuous production lines are used, and they are completed through many processes such as decoiling, degreasing, rinsing, drying, furnace annealing, spray cooling, and winding. This kind of equipment is complex in structure and expensive. At present, our country adopts the periodic annealing furnace. The furnaces used are controlled atmosphere furnaces and vacuum furnaces. Which vacuum furnace is more convenient. Since the aluminum foil is made with oil, there are many traces of oil in the gap between the aluminum foils. The vacuum annealing has a degreasing effect, which can effectively remove the oil traces, protect the foil surface and improve the electrolytic corrosion effect of the aluminum foil. The maintenance of vacuum during annealing is the key to protecting the foil surface. After the workpiece is installed in the furnace, the vacuum degree should be pumped to lPa. During the entire annealing process, the vacuum level should be kept above lOOPa. Recrystallization annealing with a vacuum furnace can make the average grain diameter reach 0.10. Reasonable selection of vacuum heat treatment equipment Vacuum heat treatment furnace from the form of discrete, horizontal, single chamber, dual chamber, cycle, three chamber continuous and so on. Divided from the cooling method of water, oil, air-cooled and so on. From the heating material is divided into metal (molybdenum, tungsten), non-metallic (graphite). From the use of divided annealing, fire, tempering, solid solution, aging, diffusion, sintering, brazing, degreasing, cleaning, drying and so on. How to reasonably select the vacuum furnace according to the material, shape, characteristics and technical requirements of the product, except for the use of a vertical furnace where the length and diameter ratio of a thin rod-shaped part or thin-walled long cylindrical part is selected to be a vertical furnace . How to choose the type and model of the vacuum furnace according to the material and technical requirements can be roughly referred to the following table or the vacuum site 181. Vacuum furnace selection Suggested types of use Recommended models Remarks Vacuum Annealing furnace Iron and steel and other black metal annealing Electric iron, Gui steel annealing, Titanium alloy in addition to hydrogen, stress relief annealing a ft temperature alloy, elastic alloy solution, aging. WZT (molybdenum heating element) and solid solution aging fast cooling function of its empty water quenching furnace austenitic stainless steel solid solution (larger size) bark copper solid solution, nuclear industry special materials such as solid solution and water quenching. WZSC Annealing Function Vacuum Oil Quenching Furnace Alloy Structural Steel, Mould High Speed ​​Steel Quenched Austenitic Stainless Steel Solid Solution (Small Size, Thin) W2C Annealing Function Vacuum Gas Quenching Furnace Alloy Die Steel Air Cooling Quenching to Improve Gas Cooling capacity, productivity, energy saving WZDQWZDGQ WZQWZGQ and annealed solid solution aging quick cooling function vacuum tempering furnace tool steel tempering temperature alloy, elastic alloy, can strengthen the copper alloy aging. Titanium alloys, copper and copper alloys for stress relief, work hardening annealing W2H vacuum brazing furnace stainless steel, gold, silver brazing and other aluminum and aluminum alloy brazing WZQH WZLQH and annealing solid solution aging rapid cooling vacuum sintering furnace W-based hard Sintered Hydrogen Storage Material Annealing Permalloy Sintering and Annealing WZDS (Molybdenum Heating Element) and Annealing Solid Solution Aging Fast Cooling Features Vacuum Cleaning, Degreasing, Drying Furnace Parts Degreasing, Washing, Drying ZQ Vacuum Carburizing Alloys Structural steel, stainless steel carburizing quenching.
The air-cooled quenching, annealing, and decarburization of medium and high alloy tool steels will be repaired. WZST oil and oil quenching annealing, carbon replenishment Function of the letter Meaning: W (horizontal) Z (vacuum) TC annealing) SC (water quenching) C (oil quenching) D (single chamber) (pressurization) G (high pressure) H (Tempered) QH (brazing) L (aluminum) S (sintered) (air cooled) ZQ (cleaning) ST (carburizing) vacuum furnace types, models, specifications and detailed technical parameters see sample or read SS3LiEei2kL!S=n Exam 1 Li Jian, Clean Production and Heat Treatment, The Sixth National Symposium on Heat Treatment and Energy Saving Technology Exchange Symposium P6 2 Yi Canian, Development of Gas Radiant Tube Vacuum Heat Treatment Furnaces, Industrial Heating (Japan) Vol.32, No.6 3 Liu Zhiqun Etc., vacuum heat treatment technology applied to special miniature bearings, etc., Shanghai Miniature Bearing Factory, 1983 4 Yuan Peibai, vacuum heat treatment of aviation titanium alloy parts, 5th National Vacuum Heat Treatment Annual Conference Proceedings 19926P66 5 Yan Fang, vacuum for T4C alloy parts Analysis of Influencing Factors of Annealed Children, Proceedings of the 6th National Vacuum Heat Treatment Annual Conference 1995.6.P135 6 Yang Fengxiang, Improvement of Electrotechnical Pure Iron Annealing Process Parameters by Vacuum Furnace, Sixth National Vacuum Heat Treatment Conference Paper Set 1995.6.P85 7 Feng Fafu et al., Effect of Vacuum Heat-treated Brass Products, Proceedings of the Fifth National Conference on Vacuum Heat Treatment 1992.6.P102
Aluminum sand casting production technology process:
The precision of the Aluminum sand casting: ±1mm;
Smoothness of surface of rough part: Ra6.4;
Shrinkage rate of aluminum sand casting products: 2%;
Material wastage rate: 7%;
General aluminum sand casting machining allowance: 2mm~3mm;
Surface preparation methods: Sand blasted, Shot blasting, Powder coating, Painting, Plating, Electrophoresis, Polishing.
Advantages and disadvantages of aluminum sand casting part:
Generally use wooden and aluminum mold, far cheaper than metal mold casting mould. The price advantage is particularly prominent in small batch and bulk production. But the production efficiency is low; Low dimension accuracy of castings, the surface is rough.
The production of aluminum sand casting parts
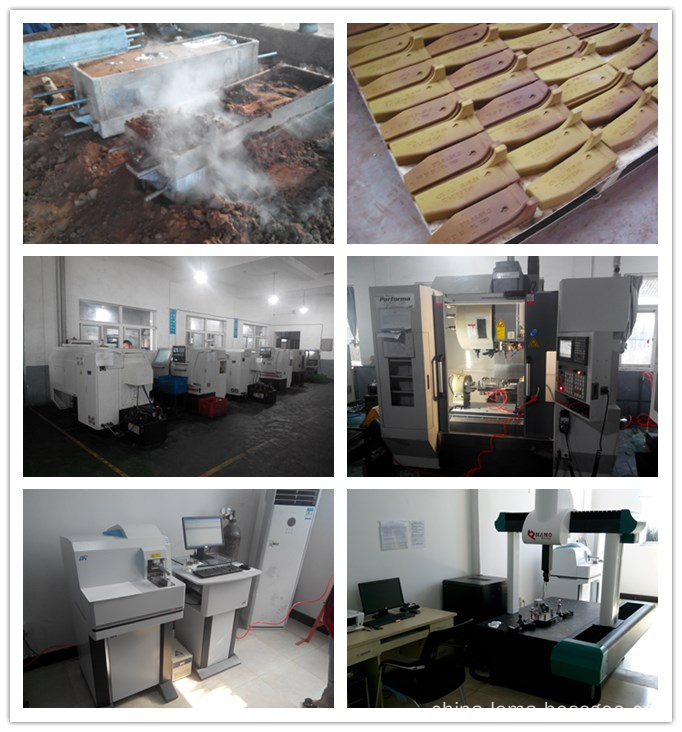

Aluminum Sand Casting Part, Aluminum Foundry Casting Part, A356 Sand Casting Part, ZL101 Sand Casting Product, Aluminum Sand Cast Part, A356 T6 Sand Casting
NINGBO BEILUN LEMA MACHINERY TECHNOLOGY CO.,LTD , http://www.china-lema.com